Work over the past three decades has greatly advanced our understanding of the regulation of Kir K+ channels by polyanionic lipids of the phosphoinositide (e.g., PIP2) and fatty acid metabolism (e.g., oleoyl-CoA). However, comparatively little is known regarding the regulation of the K2P channel family by phosphoinositides and by long-chain fatty acid–CoA esters, such as oleoyl-CoA. We screened 12 mammalian K2P channels and report effects of polyanionic lipids on all tested channels. We observed activation of members of the TREK, TALK, and THIK subfamilies, with the strongest activation by PIP2 for TRAAK and the strongest activation by oleoyl-CoA for TALK-2. By contrast, we observed inhibition for members of the TASK and TRESK subfamilies. Our results reveal that TASK-2 channels have both activatory and inhibitory PIP2 sites with different affinities. Finally, we provided evidence that PIP2 inhibition of TASK-1 and TASK-3 channels is mediated by closure of the recently identified lower X-gate as critical mutations within the gate (i.e., L244A, R245A) prevent PIP2-induced inhibition. Our findings establish that K+ channels of the K2P family are highly sensitive to polyanionic lipids, extending our knowledge of the mechanisms of lipid regulation and implicating the metabolism of these lipids as possible effector pathways to regulate K2P channel activity.
Introduction
Members of the large family of two-pore domain potassium (K2P) channels are critically involved in many cellular functions ranging from renal ion homeostasis, cell development, hormone secretion, and immune functions as well as cardiac and neuronal excitability (Enyedi and Czirják, 2010). Accordingly, dysregulation of K2P channels is seen in many disease states, such as cardiac disorders (i.e., atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia; Liang et al., 2014; Decher et al., 2017b), hyperaldosteronism (Davies et al., 2008; Bandulik et al., 2015), and pulmonary arterial hypertension (Olschewski et al., 2006; Ma et al., 2013; Antigny et al., 2016), as well as in pain perception disorders, such as migraine and depression (Alloui et al., 2006; Heurteaux et al., 2006; Lafrenière et al., 2010; Andres-Enguix et al., 2012; Royal et al., 2019). Initially thought to mediate passive background conductance in excitable cells, increasing evidence shows that K2P channels are highly regulated by sensing a broad range of diverse physiological stimuli and endogenous ligands. However, not all K2P channels respond to the same set of stimuli; rather, their sensitivity profile corresponds to their affiliation with one of the known six subfamilies (TREK, TASK, TALK, THIK, TWIK, and TRESK). Members of the TREK subfamily (TREK-1, TREK-2, and TRAAK) display the most diverse (and, e.g., regarding TREK-1, the best investigated) regulation, with relevant stimuli including temperature (Maingret et al., 2000a), mechanical force (Maingret et al., 1999; Chemin et al., 2005), membrane voltage (Maingret et al., 2002; Schewe et al., 2016), extracellular/intracellular pH (Maingret et al., 1999; Honoré et al., 2002), partner proteins (Plant et al., 2005; Sandoz et al., 2006), and various lipids (Maingret et al, 2000b; Chemin et al, 2005, 2007). Members of the TALK subfamily (TASK-2, TALK-1, and TALK-2) are activated by high extracellular pH (Morton et al., 2003; Duprat et al., 2005; Niemeyer et al., 2010). TASK-1, TASK-3, and TASK-5 make up the TASK subfamily, and members are inhibited by extracellular acidification (Rajan et al., 2000; Bayliss et al., 2001; Morton et al., 2003) but also respond to membrane lipids such as diacylglycerol (DAG; Wilke et al., 2014). Members of the TWIK subfamily (TWIK-1, TWIK-2, and TWIK-3) are rather stimuli insensitive, but their cellular activity is controlled by regulated protein trafficking (Feliciangeli et al., 2007; Feliciangeli et al., 2010) as well as possibly SUMOylation (Rajan et al., 2005; Plant et al., 2010) and unique features of the selectivity filter (SF) gate (Nematian-Ardestani et al., 2020). The TRESK subfamily has just one member (i.e., TRESK) and is regulated in particular by changes in intracellular Ca2+ levels mediated by the calmodulin-dependent phosphatase calcineurin (Czirják et al., 2004). For the THIK subfamily (THIK-1 and THIK-2), no physiological gating stimulus has been reported so far.
Work of the last three decades revealed that many ion channels are regulated by phosphoinositides and in particular by the most abundant phosphoinositide, phosphoinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2; PIP2). PIP2-sensitive channels include all members of the inward-rectifying potassium (Kir) channels (Suh and Hille, 2005; Logothetis et al., 2007; Suh and Hille, 2008) but also members of the voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels (Oliver et al., 2004; Rodriguez et al., 2010; Kruse et al., 2012; Zaydman and Cui, 2014; Taylor and Sanders, 2017), transient receptor potential (TRP) cation channels (Qin, 2007; Suh and Hille, 2008), Ca2+-activated BK-type channels (Vaithianathan et al., 2008), hyperpolarization-activated and cyclic nucleotide–gated channels (Pian et al., 2006; Zolles et al., 2006; Ying et al., 2011), and a number of ion transporters (i.e., NCX, NCE, PMCA; Hilgemann et al., 2001; Gamper and Shapiro, 2007). Many physiologically important processes, such as insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells (Rorsman and Ashcroft, 2018) or mechanical transduction and adaptation in hair cells (Hirono et al., 2004; Effertz et al., 2017), involve the regulation of ion channels by phosphoinositides. The mechanisms of regulation in some of these channels have been resolved to the atomic level (Hansen et al., 2011; Niu et al., 2020; Sun and MacKinnon, 2020).
The first report on the regulation of a K2P channel by phosphoinositides dates to 2005 and still represents an important reference on this topic (Chemin et al., 2005). Chemin and colleagues reported the strong activation of TREK-1 channels by several phospholipids, including phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylserine, phosphatidic acid (PA), and PIP2 (with PA being the most potent lipid), and identified a cluster of basic residues in the proximal C-terminus directly extending from TM4 as a potential PIP2 binding region (Chemin et al., 2005). Accordingly, it was proposed that negatively charged lipids (e.g., PIP2) electrostatically interact with these clustered basic residues and thereby cause channel activation (Chemin et al., 2005). Later the same authors reported that PIP2 application can also produce TREK-1 inhibition (Chemin et al, 2007). More recently, an additional potential PIP2 interaction region in the more distal C-terminus of TREK-1 channels has been suggested (Soussia et al., 2018). The direct binding of anionic lipids such as PA, phosphatidylglycerol (PG), and PIP2 to purified TREK-1 channels was demonstrated via a fluorescence binding assay (Cabanos et al., 2017) and to purified TRAAK channels by means of mass spectrometry (Schrecke et al., 2021). Furthermore, TREK-1 was shown to bind phospholipase D2 (PLD2) via its C-terminus and the local production of PA by PLD2 to produce channel activation. Interestingly, Cabanos and colleagues reported that PIP2 can displace PA and PG in TREK-1 to produce channel inhibition as measured in a liposome K+ flux assay (Cabanos et al., 2017).
Aside from the TREK subfamily, the effects of PIP2 have also been studied in TASK-1, TASK-2, TASK-3, and TRESK channels. Initially, the inhibition of TASK-1 and TASK-3 by phospholipase C (PLC) activation was thought to result from PIP2 breakdown (Lopes et al., 2005), as PIP2 appeared to cause activation; however, later it became clear that DAG (released by PLC) likely inhibits TASK-1 and TASK-3 channels directly (Wilke et al., 2014). In TASK-2 channels and human (but not rodent) TRESK channels, application of PIP2 to excised patches has been reported to cause activation (Lopes et al., 2005; Niemeyer et al., 2017; Giblin et al., 2019).
Another class of polyanionic lipids known to regulate ion channels are long-chain fatty acid coenzyme A (LC-CoA) esters. These obligate metabolites of cellular fatty acids affect many Kir channels, producing activation in KATP (Kir6.2/SUR) channels (Bränström et al., 1998; Schulze et al., 2003) but inhibition in most other Kir channels (Rapedius et al., 2005; Shumilina et al., 2006; Tucker and Baukrowitz, 2008; Cheng et al., 2011). Aside from the Kir channel family, little is known about the effects of LC-CoA on other ion channels. However, TRPV1 channels have been reported to be activated by LC-CoA (Yu et al., 2014). In both, Kir channels and TRPV1, LC-CoA appears to interact with the same sites that also bind PIP2, likely via the negative phosphate groups present in both types of lipids (Schulze et al., 2003; Yu et al., 2014).
Aside from the aforementioned exception of TREK/TRAAK, TASK-1/-2/-3, and TRESK channels, effects of phosphoinositides on other members of the K2P channel family have not been investigated yet, and K2P channel regulation by LC-CoA is so far unexplored. Therefore, we systematically studied the effect of PIP2 and LC-CoA on K2P channels by testing all functionally expressing channels (12 out of 15) under identical conditions and quantified their respective sensitivities. We uncovered that all K2P channel members strongly respond to at least one of the two polyanionic lipid species and that the six K2P channel subfamilies can be classified as either polyanionic lipid-activated or lipid-inhibited subfamilies. Furthermore, we investigated the physicochemical prerequisites for lipid activation in TALK-2 channels and the structural regulation mechanism of lipid regulation in the TASK subfamily. We finally discuss the potential physiological relevance of our findings that, however, warrant further investigation in more native preparations.
Materials and methods
Molecular biology and oocyte expression
For this study, we used the coding sequences of hTWIK-1 (GenBank accession no. NM_002245.3), hTREK-1 (NM_172042.2), rTREK-1 (NM_172041.2), hTREK-2 (NM_138318.2), hTRAAK (AF_247042.1), hTALK-1 (NM_032115.4), hTALK-2 (EU978944.1), hTASK-2 (NM_003740.3), hTASK-1 (NM_002246.2), hTASK-3 (XM_011517102.1), hTHIK-1 (NM_022054), hTHIK-2 (NM_022055.1), and hTRESK (NM_181840.1). To increase surface expression and macroscopic currents, measurements of TWIK-1 and THIK-2 channels were performed using channels with mutated retention motifs and a known activating mutation hTHIK-2, respectively (TWIK-1 I293A/I294A [TWIK-1*] and THIK-2 R11A/R12A/R14A/R15A/R16A/A155P [THIK-2*]). All mutant channels were obtained by site-directed mutagenesis with custom oligonucleotides. All constructs were subcloned into the pFAW dual-purpose vector suitable for in vitro transcription/oocyte expression and transfection of cultured cells and verified by sequencing. cRNA was synthetized using AmpliCap-Max T7 or SP6 High Yield Message Maker Kits (CELLSCRIPT) and stored at −20°C (for frequent use) and −80°C (for long-term storage). Xenopus laevis oocytes were surgically removed from adult female frogs and treated with type II collagenase before manual defolliculation. Oocytes were injected with ∼50 nl of channel-specific cRNA (0.5–1 µg µl−1) and incubated at 17°C for 1–14 d before experimental use.
Cell culture
HEK293 cells were cultured in DMEM, supplemented with 10% FCS and 10 U ml−1 penicillin and 10 mg ml−1 streptomycin in a 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37°C. The cells were transiently transfected with Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) in 24-well plates. For electrophysiological recordings, the transfected cells were trypsinized at least 4 h before electrophysiological measurements and seeded onto sterile 10-mm coverslips in 35-mm culture dishes in antibiotic-free DMEM.
Electrophysiology
Currents were recorded from inside-out membrane patches excised from cRNA-injected Xenopus oocytes or from transiently transfected HEK293 cells at room temperature (21–23°C). For oocyte measurements, pipettes were made from thick-walled borosilicate glass capillaries and had resistances of 0.3–0.8 MΩ. Pipettes were filled with a standard pipette solution (in mM): 120 KCl, 10 HEPES, and 3.6 CaCl2, pH 7.4, adjusted with KOH/HCl. Currents were recorded using an EPC9 or EPC10 amplifier (HEKA Elektronik), sampled at 10 kHz, and filtered with 3 kHz (−3 dB). The recording program was PATCHMASTER (HEKA Elektronik; version v2×73.5). The used pulse protocols were either ramps ranging from −80 to +40 or +80 mV with a duration of 1 s and intervals of 4 or 9 s, or measurements were performed using a continuous pulse at +40 mV. Solutions were applied to the cytoplasmic side of excised membrane patches via a gravity flow multibarrel application system. Standard intracellular (bath) solutions were composed of (in mM): 120 KCl, 10 HEPES, 2 EGTA, and 1 pyrophosphate; pH was adjusted to pH 7.4 with KOH/HCl. 5 mg ml−1 BSA was added to obtain washout solution. Where indicated in experimental results, 120 mM KCl was replaced by 120 mM RbCl.
HEK293 cell measurements were performed in the whole-cell configuration of the patch-clamp technique using an EPC10 amplifier (HEKA Elektronik) and PATCHMASTER software (HEKA Elektronik; version v2×73.5) with a sampling rate and filter as above. The cells were stimulated by a ramp protocol from −100 to +60 mV with 1-s duration and a 5-s interpulse duration. Pipette resistances ranged from 1 to 3 MΩ, and pipettes were filled with intracellular solution (in mM): 140 KCl, 2 MgCl2, 1 CaCl2, 2.5 EGTA, and 10 HEPES, pH 7.3, adjusted with KOH/HCl. The bath contained (in mM): 135 NaCl, 5 KCl, 2 MgCl2, 2 CaCl2, 10 glucose, and 10 HEPES, pH 7.3, adjusted with NaOH/HCl. All modifying reagents were added directly to the bath to obtain the particular end concentrations. Lipids and other substances were stored as stock solutions (1–100 mM) at −20°C and diluted in the bath solution to the final concentration before measurements.
Chemicals, drugs, and lipids
LC-CoA (14:0, 16:0, 18:0, 18:1, 18:2, 18:3, 22:0) were purchased from Avanti Polar Lipids (Alabaster), and stock solutions were prepared in DMSO (1–5 mM). The PLC activator m-3m3FBS, tetrapentylammonium chloride, and L-α-PI(4,5)P2 ammonium salt (brain PI(4,5)P2, PIP2) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich/Merck, and stock solutions were prepared in DMSO (1–100 mM).
Animals (Xenopus)
The performed investigation conforms to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (National Institutes of Health Publication No. 85-23). For this study, we used female Xenopus animals (n = 25) that were accommodated at the animal breeding facility of the Christian Albrecht University of Kiel to isolate oocytes. Experiments using Xenopus toads were approved by the local ethics commission.
Data analysis
Data analysis was performed using FITMASTER (HEKA Elektronik; version v2×73.5), Microsoft Excel, and Igor Pro (version 6.3.7.2; Wavemetrics Inc.).
Recorded currents were analyzed from stable membrane patches at a voltage of +40 mV unless stated otherwise.
Data are represented throughout the article as mean ± SEM. Significance of a respective dataset was probed with an unpaired Student’s t test. P values are provided in the respective figures.
Image processing and figure design were performed using the open source vector graphic program Inkscape (GNU General Public License; Free Software Foundation, version 1.0.1; 3bc2e813f5, 2020–09-07; https://inkscape.org).
Online supplemental material
Fig. S1 shows the effect (activation/inhibition) of PIP2 applied to the intracellular side of excised patches of Xenopus oocytes expressing K2P WT and mutant channels as well as the effect of PLC-mediated PIP2 depletion on TREK-1 channels expressed in HEK293 cells. Fig. S2 shows the effect (activation/inhibition) of oleoyl-CoA applied to inside-out patches of Xenopus oocytes expressing K2P WT and mutant channels. Fig. S3 shows the concentration-dependent activation of TALK-2 K2P channels by oleoyl-CoA in inside-out patches. Table S1, Table S2, Table S3, and Table S4 contain the numerical data points depicted graphically in Fig. 1 A, Fig. 2 A, Fig. 3 D, and Fig. 4 C, respectively.
Results
PIP2 causes subtype-dependent responses (activation/inhibition) in most K2P channels
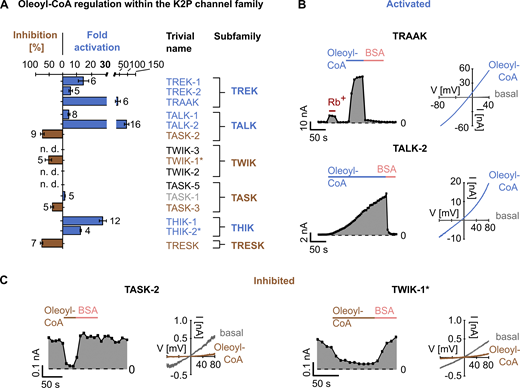
We studied the direct effect of the most abundant phosphoinositide, PI(4,5)P2 (PIP2), on all known functionally expressing K2P channels (12 in total) by applying 10 µM PIP2 to the cytoplasmatic site of the respective channels in inside-out patches excised from Xenopus oocytes. The type of response (activation or inhibition) varied depending on the K2P channel subfamily, and the efficacy of activation or inhibition depended on the particular subfamily member (Fig. 1 A and Table S1).
PIP2 regulation of K2P channels.(A) Fold activation (blue) and inhibition (percent; orange) of K2P channel currents by 10 µM PIP2 at +40 mV, measured in ramp protocols as shown in B and C. Insensitive channels are highlighted in gray. Number of independent experiments is indicated next to the bars. Data are summarized in Table S1. (B and C) Representative current traces (right) and analyzed currents at +40 mV plotted over time (left) of THIK-1 (B) and TASK-1 (C) channels measured in voltage ramps between −80 and +80 mV in excised inside-out patches of Xenopus oocytes using control bath solution and in the presence of 10 µM PIP2. (D) Analyzed TASK-2 currents at +40 mV plotted over time, measured as in B and C, using control bath solution and in the presence of 0.1 µM or 10 µM PIP2. Current rundown is indicated with an arrow. Low PIP2 concentration (0.1 µM) rescues current rundown (right) but produces no inhibition (middle); 10 µM PIP2 also rescues rundown if present (left) but leads to a subsequent inhibition of the channel. If no rundown is present, 10 µM PIP2 only leads to inhibition (middle). All data are presented as mean ± SEM. n. d., not determined.
PIP2 regulation of K2P channels.(A) Fold activation (blue) and inhibition (percent; orange) of K2P channel currents by 10 µM PIP2 at +40 mV, measured in ramp protocols as shown in B and C. Insensitive channels are highlighted in gray. Number of independent experiments is indicated next to the bars. Data are summarized in Table S1. (B and C) Representative current traces (right) and analyzed currents at +40 mV plotted over time (left) of THIK-1 (B) and TASK-1 (C) channels measured in voltage ramps between −80 and +80 mV in excised inside-out patches of Xenopus oocytes using control bath solution and in the presence of 10 µM PIP2. (D) Analyzed TASK-2 currents at +40 mV plotted over time, measured as in B and C, using control bath solution and in the presence of 0.1 µM or 10 µM PIP2. Current rundown is indicated with an arrow. Low PIP2 concentration (0.1 µM) rescues current rundown (right) but produces no inhibition (middle); 10 µM PIP2 also rescues rundown if present (left) but leads to a subsequent inhibition of the channel. If no rundown is present, 10 µM PIP2 only leads to inhibition (middle). All data are presented as mean ± SEM. n. d., not determined.
Robust PIP2 activation was observed within the TREK subfamily with 17 ± 3-fold, 11 ± 4-fold, and 114 ± 24-fold activation for TREK-1, TREK-2, and TRAAK, respectively (Fig. 1 A). The PIP2-activated currents displayed mildly outward-rectifying I-V relationships between −80 mV and +40 mV (Fig. S1, A–C).
Representative traces of the PIP2 regulation of K2P channels and PLC-mediated inhibition of TREK-1 channels. (A–J) Representative current traces (right) and analyzed currents at +40 mV plotted over time (left) of PIP2-activated (blue) TREK-1 (A), TREK-2 (B), TRAAK (C), TALK-1 (D), TALK-2 (E), THIK-2*- and PIP2-inhibited (orange) TASK-3 (G), and TASK-2 K245A (J) K2P channels. TWIK-1* (F) and TRESK (I) are not affected by PIP2. Currents were measured in voltage ramps between −80 and +80 mV in excised inside-out patches of Xenopus oocytes using K+ or Rb+ (red) bath solutions and in the presence of 10 µM PIP2 or DMSO (1%) added to the standard K+ solution. (K) Representative traces of TREK-1 currents in whole-cell experiments using HEK293 cells measured in voltage ramps between −100 and +60 mV and analyzed at 0 mV. Measurements were performed in control solution and in the presence of 20 µM of the PLC activator m-3M3FBS. Additionally, the temperature was increased to 37°C (red) and subsequently decreased (blue) to room temperature of 21°C (blue).
Representative traces of the PIP2 regulation of K2P channels and PLC-mediated inhibition of TREK-1 channels. (A–J) Representative current traces (right) and analyzed currents at +40 mV plotted over time (left) of PIP2-activated (blue) TREK-1 (A), TREK-2 (B), TRAAK (C), TALK-1 (D), TALK-2 (E), THIK-2*- and PIP2-inhibited (orange) TASK-3 (G), and TASK-2 K245A (J) K2P channels. TWIK-1* (F) and TRESK (I) are not affected by PIP2. Currents were measured in voltage ramps between −80 and +80 mV in excised inside-out patches of Xenopus oocytes using K+ or Rb+ (red) bath solutions and in the presence of 10 µM PIP2 or DMSO (1%) added to the standard K+ solution. (K) Representative traces of TREK-1 currents in whole-cell experiments using HEK293 cells measured in voltage ramps between −100 and +60 mV and analyzed at 0 mV. Measurements were performed in control solution and in the presence of 20 µM of the PLC activator m-3M3FBS. Additionally, the temperature was increased to 37°C (red) and subsequently decreased (blue) to room temperature of 21°C (blue).
Members of the THIK subfamily were also activated by PIP2 with strong activation (19 ± twofold) for THIK-1 and weaker activation (4 ± onefold) for THIK-2*, and the activated currents showed approximately linear I-V relationships (Fig. 1, A and B; Fig. S1 H). To increase surface expression, measurements of THIK-2 channels were performed using mutated channels with a removed retention motif and a point mutation in TM2 (R11A/R12A/R14A/R15A/R16A/A155P; THIK-2*; Bichet et al., 2015).
In the TALK subfamily PIP2 caused a 4 ± 1-fold activation of TALK-2 and a weaker activation (1.7 ± 0.2-fold) of TALK-1 currents (Fig. 1 A; Fig. S1, D and E). The effect on TASK-2 was more complex and depended on the experimental history. In many excised patches, TASK-2 currents showed strong current rundown, and the application of 10 µM PIP2 produced initially a 2.4 ± 0.3-fold activation. However, this activation ceased with time, and channel activity finally dropped below the starting level, resulting in an effective PIP2 inhibition of 83 ± 3% (Fig. 1, A and D, left panel). In membrane patches lacking current rundown, PIP2 application (10 µM) caused inhibition without the initial activation (Fig. 1 D, middle panel). Furthermore, lower PIP2 concentrations (e.g., 0.1 µM) prevented current rundown (Fig. 1 D, middle panel) and activated rundown currents without producing subsequent inhibition (Fig. 1 D, right panel). These findings might indicate two distinct regulatory sites in TASK-2, with lower PIP2 levels supporting basal channel activity via an activatory site and higher PIP2 levels causing inhibition, possibly via a distinct inhibitory site.
In the TWIK subfamily, only TWIK-1* was expressed functionally but lacked a PIP2 response (Fig. 1 A and Fig. S1 F). To increase surface expression, measurements of TWIK-1 were performed using channels with a mutated retention motif (TWIK-1 I293A/I294A; TWIK-1*; Bichet et al., 2015).
Likewise, no significant PIP2 response was observed in TRESK channels (the only member of this K2P channel subfamily; Fig. 1 A and Fig. S1 I), in contrast to a previous report (Giblin et al., 2019).
Finally, in the TASK subfamily, only TASK-1 and TASK-3 were expressed functionally (TASK-5 is nonfunctional; Ashmole et al., 2001), and both channels showed marked inhibition (82 ± 2% and 61 ± 4%) upon PIP2 application (Fig. 1, A and C; Fig. S1 G).
In summary, the application of PIP2 had effects on 10 of the 12 K2P channels investigated, with only TWIK-1* and TRESK lacking any observable effect upon the addition of PIP2. Members of the TREK, THIK, and TALK subfamilies were activated by PIP2 (TASK-2 only initially), whereas members of the TASK subfamily were inhibited.
Most K2P channels are highly sensitive to the fatty acid metabolite oleoyl-CoA
We further explored the K2P channel lipid sensitivity by testing the polyanionic lipid oleoyl-CoA, which represents a common cellular long-chain fatty acid metabolite. It is known to regulate ion channels (Rapedius et al., 2005; Ventura et al., 2005; Shumilina et al., 2006); however, it has not been investigated in K2P channels so far. Upon application of 10 µM oleoyl-CoA, strong activation of TREK-1 (15 ± threefold) and weaker activation of TREK-2 (6 ± onefold) were observed (Fig. 2 A; Fig. S2, A and B; and Table S2). Notably, as seen with PIP2 (Fig. 1 A; Fig. S1 C), TRAAK showed the highest lipid sensitivity within its subgroup, with oleoyl-CoA causing a 40 ± 16–fold current increase (Fig. 2, A and B). Furthermore, these activations were readily reversed upon extraction of oleoyl-CoA via the fatty acid binding protein BSA (Fig. 2 B; Fig. S2, A and B).
Oleoyl-CoA regulation of K2P channels.(A) Fold activation (blue) and inhibition (percent; brown) of K2P channels at +40 mV by 10 µM oleoyl-CoA measured as in B and C. Insensitive channels are highlighted in gray. Number of independent experiments is indicated next to the bars. Data are summarized in Table S2. (B) Representative current traces (right) and analyzed currents at +40 mV plotted over time (left) of TRAAK and TALK-2 channels measured in voltage ramps between −80 and +80 mV in excised inside-out patches of Xenopus oocytes using control bath solution and in the presence of 10 µM oleoyl-CoA or 5 mg ml−1 BSA. (C) Representative current traces of TASK-2 and TWIK-1* channels measured and analyzed as in B. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. n. d., not determined.
Oleoyl-CoA regulation of K2P channels.(A) Fold activation (blue) and inhibition (percent; brown) of K2P channels at +40 mV by 10 µM oleoyl-CoA measured as in B and C. Insensitive channels are highlighted in gray. Number of independent experiments is indicated next to the bars. Data are summarized in Table S2. (B) Representative current traces (right) and analyzed currents at +40 mV plotted over time (left) of TRAAK and TALK-2 channels measured in voltage ramps between −80 and +80 mV in excised inside-out patches of Xenopus oocytes using control bath solution and in the presence of 10 µM oleoyl-CoA or 5 mg ml−1 BSA. (C) Representative current traces of TASK-2 and TWIK-1* channels measured and analyzed as in B. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. n. d., not determined.
Oleoyl-CoA regulation of K2P channels. (A–H) Representative current traces (right) and analyzed currents at +40 mV plotted over time (left) of oleoyl-CoA–activated (light blue) TREK-1 (A), TREK-2 (B), TALK-1 (C), TASK-1 (D), THIK-1 (F), and THIK-2* (G) and oleoyl-CoA–inhibited (brown) TASK-3 (E) and TRESK (H) K2P channels. Currents were measured in voltage ramps between −80 and +80 mV in excised inside-out patches of Xenopus oocytes using K+ or Rb+ (red) bath solutions and in the presence of 10 µM PIP2 or 5 mg ml−1 BSA (pink) added to the standard K+ solution.
Oleoyl-CoA regulation of K2P channels. (A–H) Representative current traces (right) and analyzed currents at +40 mV plotted over time (left) of oleoyl-CoA–activated (light blue) TREK-1 (A), TREK-2 (B), TALK-1 (C), TASK-1 (D), THIK-1 (F), and THIK-2* (G) and oleoyl-CoA–inhibited (brown) TASK-3 (E) and TRESK (H) K2P channels. Currents were measured in voltage ramps between −80 and +80 mV in excised inside-out patches of Xenopus oocytes using K+ or Rb+ (red) bath solutions and in the presence of 10 µM PIP2 or 5 mg ml−1 BSA (pink) added to the standard K+ solution.
Similar to the PIP2 responses, THIK-1 channels were strongly activated by oleoyl-CoA (29 ± 2-fold), whereas activation in THIK-2* was weaker (13.0 ± 0.4-fold; Fig. 2 A; Fig. S2, F and G).
In the TALK subfamily, TALK-2 stood out as oleoyl-CoA produced massive activation (94 ± 14-fold), while TALK-1 was only moderately activated (5 ± 1-fold; Fig. 2, A and B; Fig. S2 C). In contrast, TASK-2 channels were inhibited by oleoyl-CoA (70 ± 7%; Fig. 2, A and C), again similar to the PIP2 effects.
In the TASK subfamily, TASK-3 channels were inhibited by oleoyl-CoA (39 ± 5%) in contrast to TASK-1 channels that were rather slightly activated (Fig. 2 A; Fig. S2, D and E).
In the TWIK and TRESK subfamilies, both expressing members (i.e., TWIK-1* and TRESK) were markedly (∼50 to ∼75%) inhibited by oleoyl-CoA (Fig. 2, A and C; Fig. S2 H). As seen with all oleoyl-CoA effects reported here, application of BSA reversed the action of oleoyl-CoA.
In summary, with the exception of TASK-1, oleoyl-CoA application modulated the activity of all K2P channels tested. Furthermore, the subfamily-specific response (i.e., activation versus inhibition) resembled the effects observed with PIP2 in most cases. Exceptions to this rule were seen (1) for TASK-1, which was inhibited by PIP2 but not by oleoyl-CoA, and (2) for TWIK-1* and TRESK, which were inhibited by oleoyl-CoA but lacked PIP2 sensitivity.
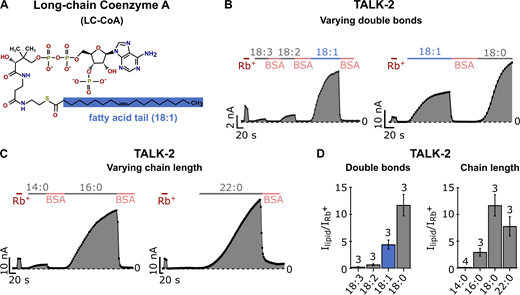
Physicochemical requirements of LC-CoA activation in TALK-2 channels
Given the particularly high sensitivity of TALK-2 to oleoyl-CoA (Fig. 3 A), we chose this channel to explore the LC-CoA properties required for activation in more detail. Throughout the following measurements, we used Rb+ activation in the beginning of each experiment for better quantification of the TALK-2–specific currents and BSA in the bath solution to accelerate the washout of oleoyl-CoA. We measured oleoyl-CoA activation for different concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 30 µM (Fig. S3, A and B), suggesting a half-maximal effect at a concentration of ∼10 µM (Fig. S3 B). Notably, even concentrations as low as 100 nM already produced robust (>3-fold) TALK-2 channel activation (Fig. S3 A), consistent with the high maximal effect (i.e., >90-fold activation) at saturating concentrations (Fig. S3 B). Furthermore, the potency to activate TALK-2 channels negatively correlated with the number of LC-CoA double bonds present in fatty acids of 18–carbon atom chain length, with the saturated stearic acid being the most potent LC-CoA (Fig. 3, B and D). Moreover, for saturated fatty acids, the strongest activation was observed for stearyl-CoA, with shorter palmityl-CoA and longer docosanoyl-CoA being less potent (Fig. 3, C and D; and Table S3). These results (except the activity drop for docosanoyl-CoA) are qualitatively consistent with the notion that increasing acyl-chain length or reducing the number of double bonds is expected to promote LC-CoA membrane incorporation and thus would result in higher effective concentrations in the membrane from whence channel interactions are likely to occur. The drop of potency for docosanoyl-CoA (compared with stearyl-CoA) apparently conflicts with this simple concept, suggesting that possibly specific interactions of the fatty acid chain with the TALK-2 channel or changes in bilayer properties might also be important.
Physicochemical properties of LC-CoA esters required for activation of TALK-2 K2P channels.(A) Chemical structure of LC-CoA (oleoyl-CoA; 18:1). The fatty acid tail is shaded blue. (B) Analyzed current traces at +80 mV of TALK-2 channels measured in voltage ramps between −80 and +80 mV in excised inside-out patches of Xenopus oocytes using control bath solution and in the presence of 3 µM of LC-CoA esters with varying number and position of double bonds (18:0, 18:1, 18:2, 18:3) in the fatty acid tail of the molecule or 5 mg ml−1 BSA. (C) Analyzed current traces at +80 mV of TALK-2 channels, measured as in B, using control bath solution and in the presence of 3 µM LC-CoA esters with varying chain length (14:0, 16:0, 18:0, 22:0) of the fatty acid tail. (D) Fold activation of TALK-2 channels by LC-CoA esters with varying double bonds or chain lengths, measured as in B and C and normalized to the respective Rb+-activated current (red; B and C) at +80 mV. Data are summarized in Table S3. The average fold activation by Rb+ (I+Rb/Ibasal) of TALK-2 WT channels is 12 ± 3 (n = 20). Number of independent experiments is indicated above the bars. All data are presented as mean ± SEM.
Physicochemical properties of LC-CoA esters required for activation of TALK-2 K2P channels.(A) Chemical structure of LC-CoA (oleoyl-CoA; 18:1). The fatty acid tail is shaded blue. (B) Analyzed current traces at +80 mV of TALK-2 channels measured in voltage ramps between −80 and +80 mV in excised inside-out patches of Xenopus oocytes using control bath solution and in the presence of 3 µM of LC-CoA esters with varying number and position of double bonds (18:0, 18:1, 18:2, 18:3) in the fatty acid tail of the molecule or 5 mg ml−1 BSA. (C) Analyzed current traces at +80 mV of TALK-2 channels, measured as in B, using control bath solution and in the presence of 3 µM LC-CoA esters with varying chain length (14:0, 16:0, 18:0, 22:0) of the fatty acid tail. (D) Fold activation of TALK-2 channels by LC-CoA esters with varying double bonds or chain lengths, measured as in B and C and normalized to the respective Rb+-activated current (red; B and C) at +80 mV. Data are summarized in Table S3. The average fold activation by Rb+ (I+Rb/Ibasal) of TALK-2 WT channels is 12 ± 3 (n = 20). Number of independent experiments is indicated above the bars. All data are presented as mean ± SEM.
Oleoyl-CoA activation of TALK-2 K2P channels. (A and B) Representative current traces (left) and analyzed currents at +80 mV plotted over time (right) of TALK-2 channels measured in voltage ramps between −80 and +80 mV in excised inside-out patches of Xenopus oocytes using K+ or Rb+ (red) bath solutions and in the presence of 0.1 µM (A), 1 µM, 3 µM, 5 µM, 10 µM, and 30 µM (B) oleoyl-CoA or 5 mg ml−1 BSA for washout.
Oleoyl-CoA activation of TALK-2 K2P channels. (A and B) Representative current traces (left) and analyzed currents at +80 mV plotted over time (right) of TALK-2 channels measured in voltage ramps between −80 and +80 mV in excised inside-out patches of Xenopus oocytes using K+ or Rb+ (red) bath solutions and in the presence of 0.1 µM (A), 1 µM, 3 µM, 5 µM, 10 µM, and 30 µM (B) oleoyl-CoA or 5 mg ml−1 BSA for washout.
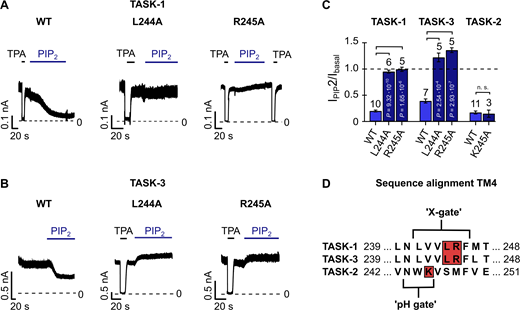
Location of the PIP2 inhibition gate in TASK-1 and TASK-3
Here, we report the inhibition of TASK-2, TASK-1, TASK-3, TWIK-1*, and TRESK by the polyanionic lipids PIP2 and oleoyl-CoA. This raises the question of the nature of the inhibition gate. Interestingly, TASK-1 and TASK-3 have previously been shown to be inhibited by DAG, and a region named the halothane response element in the distal TM4 segment was identified to be critical (Talley and Bayliss, 2002; Wilke et al., 2014). Moreover, in TASK-1, a gate at the halothane response element has recently been crystallographically identified and named the “X-gate” (Rödström et al., 2020). This X-gate forms a permeation-blocking pore constriction at the contact points of the TM4 helices, located halfway between the SF gate and the cytoplasmic pore entrance. Mutations within the lower X-gate (e.g., L244A and R245A; Fig. 4 D) have been shown to disturb channel closure, resulting in channels with a higher relative open probability (Rödström et al., 2020). Notably, we found that the mutations L244A and R245A completely abolished PIP2 inhibition in TASK-1 and TASK-3 channels (Fig. 4, A–C; and Table S4), suggesting that PIP2 induces closure of the X-gate similarly to DAG.
Mutations within the lower gate (X-gate) prevent PIP2 inhibition in TASK-1 and TASK-3 K2P channels.(A and B) Representative current traces of TASK-1 WT, L244A, and R245A mutant channels (A) and TASK-3 L244A and R245A mutant channels (B) measured at continuous +40 mV in excised inside-out patches of Xenopus oocytes using control bath solution and in the presence of 10 µM PIP2 or 1 mM tetrapentylammonium chloride (TPA), showing that mutations disrupting the lower gate render the channels insensitive to PIP2. (C) Fold change of TASK-1, TASK-3, and TASK-2 WT (light blue) and mutant (dark blue) currents analyzed at +40 mV in the presence of 10 µM PIP2 measured as in A and B, Fig. 1 D (middle panel), or Fig. S1 J. Number of independent experiments is indicated above the bars. Data are summarized in Table S4. (D) Sequence alignment of TM4 of TASK-1, TASK-3, and TASK-2 K2P channels. The lower X-gate in TASK-1 (TASK-3) and the region that forms the lower “pH gate” in TASK-2 are highlighted. Red boxes show the location of introduced mutations in the respective K2P channel. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. Data in C are analyzed by unpaired Student’s t test. P values are indicated. n. s., not significant.
Mutations within the lower gate (X-gate) prevent PIP2 inhibition in TASK-1 and TASK-3 K2P channels.(A and B) Representative current traces of TASK-1 WT, L244A, and R245A mutant channels (A) and TASK-3 L244A and R245A mutant channels (B) measured at continuous +40 mV in excised inside-out patches of Xenopus oocytes using control bath solution and in the presence of 10 µM PIP2 or 1 mM tetrapentylammonium chloride (TPA), showing that mutations disrupting the lower gate render the channels insensitive to PIP2. (C) Fold change of TASK-1, TASK-3, and TASK-2 WT (light blue) and mutant (dark blue) currents analyzed at +40 mV in the presence of 10 µM PIP2 measured as in A and B, Fig. 1 D (middle panel), or Fig. S1 J. Number of independent experiments is indicated above the bars. Data are summarized in Table S4. (D) Sequence alignment of TM4 of TASK-1, TASK-3, and TASK-2 K2P channels. The lower X-gate in TASK-1 (TASK-3) and the region that forms the lower “pH gate” in TASK-2 are highlighted. Red boxes show the location of introduced mutations in the respective K2P channel. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. Data in C are analyzed by unpaired Student’s t test. P values are indicated. n. s., not significant.
In the pH-sensitive TASK-2 channel, a lower gate at a location similar to the X-gate in TASK-1 has been identified recently in cryo-EM structures obtained at different pH (Li et al., 2020). This work identified a lysine residue (i.e., K245) within the lower gate as a pH-sensing residue and also as a critical component of the lower gate itself. However, mutation of this lysine to alanine (K245A) had no obvious effect on PIP2 inhibition in TASK-2 (Fig. 4, C and D; Fig. S2 J). This suggests either that PIP2 inhibition is mediated via a different gate (e.g., the SF) or that K245 is not critical for mediating PIP2 inhibition via the lower gate in contrast to pH inhibition.
Discussion
Our comprehensive screen established K2P channels as a family of K+ channels highly sensitive to polyanionic membrane lipids such as PIP2 and oleoyl-CoA. Furthermore, depending on the particular K2P subfamily, polyanionic lipids either produced activation (TREK, TALK, and THIK subfamilies) or inhibition (TASK, TWIK, and TRESK subfamilies). The responses evoked in a particular subfamily produced by PIP2 and oleoyl-CoA were similar, with three exceptions: (1) TWIK-1* and (2) TRESK were PIP2 insensitive but were inhibited by oleoyl-CoA, and (3) TASK-1 was inhibited by PIP2 but was oleoyl-CoA insensitive (Fig. 5 B).
Subtype-specific regulation of K2P channels by polyanionic lipids. (A) Gating cartoon depicting cross-sectional sketches of K2P channels indicating the assumed locations of the gates regulated by polyanionic lipids (i.e., PIP2 and oleoyl-CoA). In TREK-1, TREK-2, and TRAAK channels, the gate is located at the SF and opened by polyanionic lipids. In TASK-1 and TASK-3, the gate is located below the SF (lower gate/X-gate) and closed by polyanionic lipids. Note that the cartoon does not intend to indicate specific binding sites of the lipids. (B) Overview of the subtype-specific lipid effects in K2P channels: dark blue box, activation; red box, inhibition; light blue box, insensitivity to the lipids with (1) PIP2 and (2) oleoyl-CoA. The gray box indicates that the respective lipid effect was not determined (n. d.) to be caused by low functional channel expression.
Subtype-specific regulation of K2P channels by polyanionic lipids. (A) Gating cartoon depicting cross-sectional sketches of K2P channels indicating the assumed locations of the gates regulated by polyanionic lipids (i.e., PIP2 and oleoyl-CoA). In TREK-1, TREK-2, and TRAAK channels, the gate is located at the SF and opened by polyanionic lipids. In TASK-1 and TASK-3, the gate is located below the SF (lower gate/X-gate) and closed by polyanionic lipids. Note that the cartoon does not intend to indicate specific binding sites of the lipids. (B) Overview of the subtype-specific lipid effects in K2P channels: dark blue box, activation; red box, inhibition; light blue box, insensitivity to the lipids with (1) PIP2 and (2) oleoyl-CoA. The gray box indicates that the respective lipid effect was not determined (n. d.) to be caused by low functional channel expression.
Physiological implications of the PIP2 regulation in K2P channels
In the Kir channel family, most if not all members are thought to require PIP2 as a mandatory ligand to be functional (Huang et al., 1998; Logothetis et al., 2007; Fürst et al., 2014). For K2P channels, not all members are activated by PIP2, and thus PIP2 can be considered a modulatory agent rather than a mandatory ligand. Accordingly, G protein–coupled receptor (GPCR; i.e., P2Y2) activation of PLC produced strong inhibition of TREK-1 activity (i.e., activity is no longer detectable) in HEK293 cells; however, subsequent activating stimuli (e.g., temperature increase) still produced robust activation (Fig. S1 K), indicating that PIP2 is not strictly required for channel activity.
Activation of TREK-1 channels by PIP2 has been reported previously (Chemin et al, 2005, 2007; Soussia et al, 2018) as well as split responses with PIP2 causing activation and inhibition (Chemin et al, 2007). Furthermore, in liposomes, PIP2 caused inhibition of TREK-1 K+ flux in the presence of PG, suggesting that PIP2 might cause inhibition by competitive displacement of the strongly activatory lipids such as PG or PA (Cabanos et al., 2017). However, in our hands, inhibition of TREK-1/-2 channels was never observed in the Xenopus oocyte expression system. Resolving these discrepancies is difficult; however, possibly TREK-1/-2 might be liganded by strongly activatory lipids such as PA or PG to various degrees in cells, and then their competitive displacement by PIP2 might result in channel inhibition (assuming PIP2 is a less potent activator than the displaced lipid). Thus, the variable outcomes might be related to the actual lipid microenvironment or to the lipid ligandation situation at which PIP2 is added to the TREK-1 channel. Also, the interaction of TREK-1 with PLD2 (producing PA) might differ in cells. Notably, TRAAK channels do not interact with PLD2 (Comoglio et al., 2014), and PIP2 inhibition has not been reported. Here, we report that TRAAK channels exhibited the strongest PIP2 response of all K2P channels, with a >110-fold increase in channel activity. The physiological relevance of this PIP2 regulation is currently unexplored but warrants further investigation in native preparations such as neurons that strongly express TRAAK channels (Brohawn et al., 2019; Kanda et al., 2019).
A notable finding of this work is the strong activation of THIK-1 channels by PIP2 (Fig. 1, A and B). Despite its expression in many regions of the central nervous system, the specific role of THIK-1 channels is currently unknown, with the exception of microglial cells, where THIK-1 activation was shown to be involved in microglial immune surveillance and inflammatory cytokine release (Madry et al., 2018). Interestingly, PIP2 production in microglia has been reported to play a key role in immune response signaling (Nguyen et al., 2017; Desale and Chinnathambi, 2021) and thus possibly involves PIP2 activation of THIK-1.
We report here the inhibition of TASK-1 and TASK-3 channels by PIP2. The involvement of the PIP2 metabolism in the regulation of TASK-1 and TASK-3 has been intensively studied before, and it is currently assumed that GPCR-mediated release of DAG directly inhibits these channels, while the breakdown of PIP2 appears not to be critical (Bista et al., 2015). Thus, the activation of TASK-1 and TASK-3 via membrane PIP2 depletion (i.e., release of PIP2 inhibition by, e.g., PLC activation) may not be of physiological relevance. However, inhibition of TASK-1 or TASK-3 via a local or global production of PIP2 still could be a regulatory mechanism.
TASK-2 channels have previously been reported to be activated by the short-chain PIP2 derivative dioctanoyl-PIP2 (Niemeyer et al., 2017) which apparently contradicts the here reported inhibition of TASK-2 by application of the native (i.e., long-chain) PI(4,5)P2. However, we found that the PIP2 effect is clearly concentration dependent, with lower PIP2 concentrations supporting TASK-2 activity consistent with the reactivation of rundown of TASK-2 channel currents. Longer PIP2 applications as well as application on patches lacking current rundown produced robust and reliable inhibition. These findings might indicate that distinct regulatory PIP2 sites exist in TASK-2 channels (i.e., a “higher” affinity activatory PIP2 site and a “lower” affinity inhibitory PIP2 site). Accordingly, at higher PIP2 concentration, the inhibitory site dominates, causing inhibition in TASK-2 (as seen with TASK-1 and TASK-3), whereas lower PIP2 concentration supports TASK-2 activity via the higher-affinity activatory site. However, these are rather speculative assumptions that clearly need further investigation.
It should also be pointed out that we provide only qualitative information on the effects of PIP2 on the various channels and have not demonstrated direct channel PIP2 interaction. Accordingly, we cannot rule out the possibility that PIP2 might have affected the investigated K2P channels also via indirect mechanisms such as (1) changes in bilayer properties, (2) binding to accessory proteins, or (3) lipid metabolites (e.g., PA, DAG, arachidonic acid [AA]) produced by enzymes contained in an excised patch and initiated by the addition of PIP2. For instance, PIP2 is known to activate PLD2 (Bowling et al., 2020), which would indirectly activate TREK-1 through PA or PG production.
Physiological implications of the LC-CoA regulation in K2P channels
LC-CoA represents ubiquitous cellular products of the fatty acid metabolism as fatty acids bound to CoA before they can be taken up by mitochondria for β-oxidation. Our study revealed the regulation of many K2P channels by oleoyl-CoA. LC-CoA has previously been reported to modulate several members of the Kir channel family (Larsson et al., 1996; Rohács et al., 2003; Rapedius et al., 2005; Shumilina et al., 2006; Tucker and Baukrowitz, 2008). KATP channels are thereby strongly activated, while most other Kir channels are inhibited, likely because LC-CoA competes with PIP2 for binding but lacks its activatory effect (competitive antagonism; Shumilina et al., 2006). Such competitive antagonism, however, is unlikely to cause the here reported inhibition in TASK-2, TASK-1, TASK-3, TWIK, and TRESK channels because these channels were not activated by PIP2. However, in the PIP2-activated channels (e.g., TREK-1), oleoyl-CoA likely interacts with the same sites as PIP2 because the degree of oleoyl-CoA and PIP2 activation is correlated in most K2P channels.
The role of LC-CoA activation of KATP channels has been implicated in the mechanism of insulin secretion in pancreatic β cells, in fatty acid sensing in hypothalamic neurons, and in protection of cardiac myocytes under ischemic condition (Corkey et al., 2000; Liu et al., 2001; Tarasov et al., 2004; Le Foll et al., 2009; Rorsman and Ashcroft, 2018). These situations have in common that they cause an accumulation of LC-CoA in the cytoplasm, which potentially could also modulate the activity of the K2P channels present in the respective tissues.
TALK-2 and TREK-1 channels are expressed in atrial as well as ventricular myocytes in the heart (Decher et al., 2001; Tan et al., 2004; Decher et al., 2017a). These channels are highly sensitive to LC-CoA as oleoyl-CoA caused a >15-fold activation (Fig. 2, A and B; Fig. S1, A and E). Therefore, activation of TALK-2 and TREK-1 channels under ischemic conditions may have cardioprotective effects in ventricular myocytes by shortening of action potential and concomitant reduction in Ca2+ loading (similar to KATP channels). However, this ischemic activation of TALK-2 and TREK-1 in the atrium causing action potential shortening could also potentially be arrhythmogenic.
It is noteworthy that TALK-2 (together with TALK-1) is expressed in pancreatic β-cells, but its physiological role is currently unknown (Duprat et al., 2005; Rorsman and Ashcroft, 2018; Graff et al., 2021). Thus, the accumulation of LC-CoA under conditions of hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia could contribute to the known insulin secretion defects under these conditions because K+ channel activation is expected to antagonize insulin secretion. Notably, the sensitivity of TALK-2 to oleoyl-CoA is higher than that of KATP channels because 10 nM oleoyl-CoA produced only little activation in KATP channels, whereas we report here robust activation for TALK-2 with this concentration (Larsson et al., 1996). Currently, rather little is known about the free concentrations of LC-CoA in cells, but calculations suggest a concentration in the range of 0.1 to 200 nM (Knudsen et al., 2000). Thus, our screening concentration of oleoyl-CoA (10 µM) is certainly very high, and more work is required to demonstrate the physiological relevance of the LC-CoA regulation in K2P channels.
Structural insights into the mechanism of polyanionic lipid regulation
Based on crystallographic and functional data, it has been proposed that K2P channels are regulated primarily via a highly dynamic SF gate located at the extracellular pore entrance (Bagriantsev et al., 2011; Piechotta et al., 2011; Bagriantsev et al., 2012; Schewe et al., 2016; Schewe et al., 2019) or via lipid binding below the SF blocking ion permeation (Brohawn et al., 2014). However, more recent structural studies revealed constriction sites in the ion permeation pathway below the SF in TASK-2 and TASK-1 channels (Li et al., 2020; Rödström et al., 2020). This raises the question of which of the two possible gating structures is relevant in the context of the here reported polyanionic lipid regulation in these channels (Fig. 5 A). In the TREK subfamily, the PIP2/LC-CoA activation gate is likely the SF because lipid activation causes the transition of the voltage-dependent ion flux gating mode of the SF into the leak mode displaying a linear I-V (Fig. 2 B; Fig. 5 A; Fig. S1, A–C; Fig. S2, A and B; Schewe et al., 2016). However, THIK-1 channels display comparably little voltage gating, and thus the principal role of the SF gate is unresolved, and further experiments are required to determine the location of the PIP2/LC-CoA activation gate. Likewise, the structural mechanism of TRESK channel inhibition by LC-CoA requires further investigation.
For TASK-1 and TASK-3 channels, our experiments suggest that inhibition by PIP2 and LC-CoA involves the lower X-gate crystallographically identified in TASK-1 channels (and assumed for TASK-3 channels), as the published mutations within this region also abolished PIP2 inhibition in both channels. However, the location of the PIP2/LC-CoA binding sites, as well as the possible overlap with the still unknown inhibitory DAG binding site, will require further investigation. In TASK-2 channels, a lower gate mediating pH inhibition was recently identified in cryo-EM structures at a location similar to the X-gate in TASK-1 (Li et al., 2020). Although its involvement in PIP2/LC-CoA inhibition seems reasonable, mutation of a critical residue at the intracellular pH gate did not affect PIP2 inhibition (Fig. 4 C and Fig. S1 J). Thus, additional studies are required to clarify the structural mechanisms of polyanionic lipid inhibition in TASK-2.
Conclusions
This work establishes common polyanionic cellular lipids such as PIP2 and LC-CoA as regulators of channel activity for all 12 functionally expressing mammalian K2P channels. We provide first insights into the location of the PIP2/LC-CoA inhibition gate in TASK-1 and TASK-3, but substantially more work is required to disclose the lipid binding sites in the various K2P channels as well as the structural mechanism underlying the polyanionic lipid regulation. Finally, investigation of the relevant signal transduction pathways in native preparations is required to demonstrate the physiological relevance of linking K2P channel activity to the complex metabolisms of phosphoinositides and fatty acids in the various tissues and cell types expressing K2P channels.
Data availability
The data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
Crina M. Nimigean served as editor.
We thank members of our laboratory for helpful comments on the manuscript and technical support of the project.
These studies were supported by funding from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft to M. Schewe and T. Baukrowitz as part of the Research Unit FOR2518, DynIon.
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Author contributions: M. Schewe and T. Baukrowitz conceived and supervised the project; E.B. Riel, B.C. Jürs, S. Cordeiro, and M. Schewe performed all patch-clamp experiments and analyzed the data; M. Musinszki created and supervised the generation of mutant channels; E.B. Riel prepared all figures; E.B. Riel, M. Schewe, and T. Baukrowitz wrote the original manuscript draft and reviewed/edited the draft; M. Schewe and T. Baukrowitz obtained funding.
References
Author notes
E.B. Riel and B.C. Jürs contributed equally to this paper.