Skip Nav Destination
Close Modal
Update search
- Title
- Author
- Author Affiliations
- Full Text
- Abstract
- Keyword
- DOI
- ISBN
- EISBN
- ISSN
- EISSN
- Issue
- Volume
- References
- Title
- Author
- Author Affiliations
- Full Text
- Abstract
- Keyword
- DOI
- ISBN
- EISBN
- ISSN
- EISSN
- Issue
- Volume
- References
- Title
- Author
- Author Affiliations
- Full Text
- Abstract
- Keyword
- DOI
- ISBN
- EISBN
- ISSN
- EISSN
- Issue
- Volume
- References
- Title
- Author
- Author Affiliations
- Full Text
- Abstract
- Keyword
- DOI
- ISBN
- EISBN
- ISSN
- EISSN
- Issue
- Volume
- References
- Title
- Author
- Author Affiliations
- Full Text
- Abstract
- Keyword
- DOI
- ISBN
- EISBN
- ISSN
- EISSN
- Issue
- Volume
- References
- Title
- Author
- Author Affiliations
- Full Text
- Abstract
- Keyword
- DOI
- ISBN
- EISBN
- ISSN
- EISSN
- Issue
- Volume
- References
NARROW
Format
Subjects
Journal
Article Type
Date
1-20 of 741
Follow your search
Access your saved searches in your account
Would you like to receive an alert when new items match your search?
1
Sort by
Journal Articles
Valentina Guarnieri, Jesmeen Maimaris, Sohilla Lotfy, Elizabeth Rivers, Stuart Adams, Kimberly Gilmour, Andrea Meinhardt, Arnold Awuah, Mercedes Selby, Daisy Shillingford, Emma Gravett, Susanne Kricke Orszulik, Waseem Qasim, David Goldblatt, Helen Braggins, Robert Chiesa, Maaike Kusters, Reem Elfeky
Journal:
Journal of Human Immunity
J Hum Immun (2026) 2 (2): e20250076.
Published: 06 February 2026
Includes: Supplementary data
Images
in Beyond survival: Multisystem long-term outcomes following HSCT in chronic granulomatous disease
> Journal of Human Immunity
Published: 06 February 2026
Figure 1. OS and EFS. (A) OS at 5–10 years (y) after transplant for our cohort (n = 42). (B) Impact on 10-year OS of matched or mismatched donor (P = 0.002) and of cGvHD (P = 0.001). (C) EFS at 5–10 years after transplant for our cohort (n = More about this image found in OS and EFS. (A) OS at 5–10 years (y) after transplant for our cohort (
Images
in Beyond survival: Multisystem long-term outcomes following HSCT in chronic granulomatous disease
> Journal of Human Immunity
Published: 06 February 2026
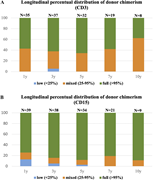
Figure 2. Posttransplant peripheral blood chimerism (n = 42). (A) Longitudinal distribution of CD3+ blood chimerism at 1, 3, 5, 7, and 10 years after transplant. (B) Longitudinal distribution of CD15+ blood chimerism at 1, 3, 5, 7, and 10 More about this image found in Posttransplant peripheral blood chimerism (n = 42). (A) L...
Images
in Beyond survival: Multisystem long-term outcomes following HSCT in chronic granulomatous disease
> Journal of Human Immunity
Published: 06 February 2026
Figure 3. Long-term specific complications (made by BioRender). More about this image found in Long-term specific complications (made by BioRender).
Journal Articles
Annelotte J. Duintjer, Robbert G.M. Bredius, J. Merlijn van den Berg, Lisette van de Corput, Willem A. Dik, Mariëlle E. van Gijn, Stefanie S. Henriet, Evelien A. Kemper, Taco W. Kuijpers, G. Elizabeth Legger, Joris M. van Montfrans, Liesbeth H. Schölvinck, Clementien L. Vermont, Els Voorhoeve, Gert Weijman, Gijs T.J. van Well, Evelien Zonneveld-Huijssoon, Mirjam van der Burg, Maartje Blom
Journal:
Journal of Human Immunity
J Hum Immun (2026) 2 (2): e20250205.
Published: 05 February 2026
Includes: Supplementary data
Images
in Managing non-SCID T cell lymphopenia after TREC-based newborn screening
> Journal of Human Immunity
Published: 05 February 2026
Figure 1. Course of lymphocyte subsets during follow-up of patients with a heterozygous FOXN1 variant identified from TREC-based NBS. The grey area represents the values between the 10th and 90th percentiles. More about this image found in Course of lymphocyte subsets during follow-up of patients with a heterozygo...
Images
in Managing non-SCID T cell lymphopenia after TREC-based newborn screening
> Journal of Human Immunity
Published: 05 February 2026
Figure 2. Course of lymphocyte subsets during follow-up of patients with idiopathic T cell lymphopenia identified from TREC-based NBS. The grey area represents the values between the 10th and 90th percentiles. More about this image found in Course of lymphocyte subsets during follow-up of patients with idiopathic T...
Journal Articles
Kanako Takeuchi, Yuichi Tateishi, Kosuke Ashihara, Takanori Utsumi, Yoshiyuki Kobayashi, Takaki Asano, Satoshi Okada
Journal:
Journal of Human Immunity
J Hum Immun (2026) 2 (2): e20250101.
Published: 04 February 2026
Includes: Supplementary data
Images
in Acute necrotizing encephalopathy associated with COVID-19 in a pediatric patient and a systematic review
> Journal of Human Immunity
Published: 04 February 2026
Figure 1. Brain CT and MRI of our patient. (A) Initial brain CT scan at disease onset showing hypoattenuation in the cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, thalamus, brainstem, and cerebellum (arrows), along with marked cerebral edema. (B) Follow-up More about this image found in Brain CT and MRI of our patient. (A) Initial brain CT scan at disease onse...
Images
in Acute necrotizing encephalopathy associated with COVID-19 in a pediatric patient and a systematic review
> Journal of Human Immunity
Published: 04 February 2026
Figure 2. EEG of our patient. In a bipolar longitudinal montage, the red curves depict the right hemisphere, the blue curves depict the left hemisphere, and the black curves depict the midline. (A) The EEG was recorded at the onset of the More about this image found in EEG of our patient. In a bipolar longitudinal montage, the red curves depi...
Images
in Acute necrotizing encephalopathy associated with COVID-19 in a pediatric patient and a systematic review
> Journal of Human Immunity
Published: 04 February 2026
Figure 3. Patient flow chart. We divided these 74 patients into two groups: (1) the severe sequelae group, which included patients who died or were in a state of brain death, and (2) the mild sequelae group, which included patients who were More about this image found in Patient flow chart. We divided these 74 patients into two groups: (1) the ...
Images
in Acute necrotizing encephalopathy associated with COVID-19 in a pediatric patient and a systematic review
> Journal of Human Immunity
Published: 04 February 2026
Figure 4. A comparison of laboratory data. (A and C) CSF protein and D-dimer tended to be higher in the death or severe sequelae group, but no significant difference was observed (A: P = 0.200, C: P = 0.076). (B) Patients in the death or More about this image found in A comparison of laboratory data. (A and C) CSF protein and D-dimer tended ...
Images
in Acute necrotizing encephalopathy associated with COVID-19 in a pediatric patient and a systematic review
> Journal of Human Immunity
Published: 04 February 2026
Figure 5. Kaplan–Meier survival curves in the severe sequelae group. (A) The Kaplan–Meier curve of the patients in the severe sequelae group (n = 14) is shown. The numbers below the Kaplan–Meier curve represent the number of patients who More about this image found in Kaplan–Meier survival curves in the severe sequelae group. (A) The Kaplan–...
Journal Articles
Qinhua Zhou, Ivan Bagarić, Fabian Komma, Chandhana Prakash, Hassan Abolhassani, Zahra Chavoshzadeh, Lulu Tsao, Taja Vatovec, Camille Soudée, Jérémie Rosain, Daniel J. Minter, Conny Lu, Nashat Al-Sukaiti, Bingbing Wu, Jinqiao Sun, Qian Zhang, Jean-Laurent Casanova, Qiang Pan-Hammarström, Alice Y. Chan, Tariq Al-Farsi, Xiaochuan Wang, Jacinta Bustamante, Jonathan Bohlen
Journal:
Journal of Human Immunity
J Hum Immun (2026) 2 (2): e20250073.
Published: 30 January 2026
Includes: Supplementary data
Journal Articles
Julie A. Jensen, Nanna Mørk, Martin Tolstrup, Ole Søgaard, Thomas Dalhuisen, Antonio Rodriguez, Rebecca Hoh, Michael J. Peluso, Steven G. Deeks, Jean-Laurent Casanova, Trine H. Mogensen
Journal:
Journal of Human Immunity
J Hum Immun (2026) 2 (2): e20250179.
Published: 30 January 2026
Includes: Supplementary data
Images
in Autoantibodies neutralizing type 1 interferons in two cohorts of people with HIV
> Journal of Human Immunity
Published: 30 January 2026
Figure 1. Baseline characteristics of the study population. The cohorts consisting of individuals from a Danish cohort (n = 318) and an American cohort (n = 292) diagnosed with HIV. Individual data at the time of inclusion for blood samples are More about this image found in Baseline characteristics of the study population. The cohorts consisting o...
Images
in Autoantibodies neutralizing type 1 interferons in two cohorts of people with HIV
> Journal of Human Immunity
Published: 30 January 2026
Figure 2. Capacity of plasma samples from individuals with HIV to neutralize IFN-I . Plasma samples from individuals with HIV-1 infection tested for their ability to neutralize five different conditions of IFN-I by applying plasma to HEK293T More about this image found in Capacity of plasma samples from individuals with HIV to neutralize IFN-I ...
Images
in Complete and partial forms of X-linked MCTS1 deficiency in patients with mycobacterial disease
> Journal of Human Immunity
Published: 30 January 2026
Figure 1. New families with MSMD and MCTS1 variants. (A) Family pedigrees with allele segregation for the four MSMD patients (black) hemizygous for the MCTS1 variants c.509T>G, c.525G>A c.164+1_164+4GTAAdel, and c.178del, who suffered from More about this image found in New families with MSMD and MCTS1 variants. (A) Family pedigrees with allel...
Images
in Complete and partial forms of X-linked MCTS1 deficiency in patients with mycobacterial disease
> Journal of Human Immunity
Published: 30 January 2026
Figure 2. Functional investigation of the new MCTS1 variants. (A) Predicted structure of the MCTS1 protein with the domain of unknown function 1947 (DUF1947) and the pseudouridine synthase and archaeosine transglycosylase (PUA) domains for WT More about this image found in Functional investigation of the new MCTS1 variants. (A) Predicted structur...
Journal Articles
Sarah Cook, Kranthi Nomula, Claire E. Cross, Hwi M. Gil, Joseph M. Choi, Saara Kaviany, James A. Connelly, Christopher C. Chang, Janet G. Markle
Journal:
Journal of Human Immunity
J Hum Immun (2026) 2 (2): e20250201.
Published: 23 January 2026
Includes: Supplementary data
1