Skip Nav Destination
Close Modal
Search Results for
Corona
Update search
- Title
- Author
- Author Affiliations
- Full Text
- Abstract
- Keyword
- DOI
- ISBN
- EISBN
- ISSN
- EISSN
- Issue
- Volume
- References
- Title
- Author
- Author Affiliations
- Full Text
- Abstract
- Keyword
- DOI
- ISBN
- EISBN
- ISSN
- EISSN
- Issue
- Volume
- References
- Title
- Author
- Author Affiliations
- Full Text
- Abstract
- Keyword
- DOI
- ISBN
- EISBN
- ISSN
- EISSN
- Issue
- Volume
- References
- Title
- Author
- Author Affiliations
- Full Text
- Abstract
- Keyword
- DOI
- ISBN
- EISBN
- ISSN
- EISSN
- Issue
- Volume
- References
- Title
- Author
- Author Affiliations
- Full Text
- Abstract
- Keyword
- DOI
- ISBN
- EISBN
- ISSN
- EISSN
- Issue
- Volume
- References
- Title
- Author
- Author Affiliations
- Full Text
- Abstract
- Keyword
- DOI
- ISBN
- EISBN
- ISSN
- EISSN
- Issue
- Volume
- References
NARROW
Date
1-20 of 283
Search Results for Corona
Follow your search
Access your saved searches in your account
Would you like to receive an alert when new items match your search?
1
Sort by
Journal Articles
Jingchao Wu, Maximilian W.D. Raas, Paula Sobrevals Alcaraz, Harmjan R. Vos, Eelco C. Tromer, Berend Snel, Geert J.P.L. Kops
Journal:
Journal of Cell Biology
J Cell Biol (2023) 223 (1): e202303007.
Published: 07 November 2023
... are temporarily covered with a dense protein meshwork known as the fibrous corona. Formed by oligomerization of ROD/ZW10/ZWILCH-SPINDLY (RZZ-S) complexes, the fibrous corona promotes spindle assembly, chromosome orientation, and spindle checkpoint signaling. The molecular requirements for formation of the fibrous...
Journal Articles
Journal:
Journal of Cell Biology
J Cell Biol (2020) 219 (5): e201905018.
Published: 24 March 2020
... is the shedding of the outermost fibrous corona layer of the kinetochore following microtubule attachment. Centromere protein F (CENP-F) is part of the corona, contains two microtubule-binding domains, and physically associates with dynein motor regulators. Here, we have combined CRISPR gene editing...
Journal Articles
Journal:
Journal of Cell Biology
J Cell Biol (1997) 139 (2): 435–447.
Published: 20 October 1997
... corona fibers that tether centromeres to the spindle. Immediately upon nuclear envelope fragmentation, an associated plus end motor trafficks cytoplasmic CENP-E toward chromosomes along astral microtubules that enter the nuclear volume. Before or concurrently with initial lateral attachment of spindle...
Images
in A farnesyl-dependent structural role for CENP-E in expansion of the fibrous corona
> Journal of Cell Biology
Published: 07 November 2023
Figure 1. Fibrous corona expansion requires CENP-E. (A) Immunostaining of ZWILCH (magenta), CENP-E (green), and CENP-C (blue) in control and CENP-E–depleted RPE1 cells treated with nocodazole overnight. Bar, 5 μm; inset bar, 1 μm. (B) Immunostaining of ZWILCH (magenta), SPINDLY (green More about this image found in Fibrous corona expansion requires CENP-E. (A) Immunostaining of ZWILCH (ma...
Images
in A farnesyl-dependent structural role for CENP-E in expansion of the fibrous corona
> Journal of Cell Biology
Published: 07 November 2023
Figure 2. Fibrous corona formation requires C-terminal farnesylation of CENP-E. (A) Domain organization of CENP-E 2111-C and various respective mutants. 2111-C fragment of CENP-E with different stretches of 10 amino acids were substituted for alanine residues or was deleted of the C-terminal 12 More about this image found in Fibrous corona formation requires C-terminal farnesylation of CENP-E. (A) ...
Images
in A farnesyl-dependent structural role for CENP-E in expansion of the fibrous corona
> Journal of Cell Biology
Published: 07 November 2023
Figure 5. Farnesylation promotes interaction of endogenous CENP-E with fibrous corona proteins in mitosis. (A) Immunostaining of ZW10 (green), CENP-E (magenta), and CENP-C (blue) in STLC-treated RPE1 cells cotreated with DMSO or GSK923295 overnight. Bar, 5 μm; inset bar, 1 μm. (B More about this image found in Farnesylation promotes interaction of endogenous CENP-E with fibrous corona...
Images
in A farnesyl-dependent structural role for CENP-E in expansion of the fibrous corona
> Journal of Cell Biology
Published: 07 November 2023
Figure 6. CENP-E impacts fibrous corona formation after initial RZZ-S kinetochore recruitment. (A) Immunostaining of ZW10 (green), CENP-E (magenta), and CENP-C (blue) in RPE1 cells treated with nocodazole for indicated time, which had been arrested with STLC and GSK923295 overnight. Bar, 5 μm More about this image found in CENP-E impacts fibrous corona formation after initial RZZ-S kinetochore rec...
Images
in A farnesyl-dependent structural role for CENP-E in expansion of the fibrous corona
> Journal of Cell Biology
Published: 07 November 2023
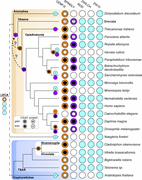
Figure 7. Comparative genomics of fibrous corona formation mechanisms in eukaryotes. Phylogenetic profiling of CENP-E, the CAAX box of CENP-E, SPINDLY, the CAAX box of SPINDLY, ROD, ZWILCH, and ZW10 across eukaryotic diversity represented by selected species. Evolutionary reconstructions More about this image found in Comparative genomics of fibrous corona formation mechanisms in eukaryotes. ...
Images
in CENP-F stabilizes kinetochore-microtubule attachments and limits dynein stripping of corona cargoes
> Journal of Cell Biology
Published: 24 March 2020
Figure 3. CENP-F controls corona localization in a microtubule-dependent manner. (a) Immunofluorescence microscopy images of early prometaphase HeLa-K, CNP-F-Mut1, and CENP-F-Mut2 cells stained with DAPI and antibodies against CENP-C and CENP-E. Scale bar, 5 µm. (b) Quantification More about this image found in CENP-F controls corona localization in a microtubule-dependent manner. (a) ...
Images
in CENP-F stabilizes kinetochore-microtubule attachments and limits dynein stripping of corona cargoes
> Journal of Cell Biology
Published: 24 March 2020
Figure 5. CENP-F functions to limit dynein stripping of the corona. (a) Left: Immunofluorescence microscopy images from the dynein-stripping assay for CENP-E in CENP-F-Mut1 cells. Cells were treated with control or DHC siRNA, arrested in nocodazole or monastrol, and stained with DAPI More about this image found in CENP-F functions to limit dynein stripping of the corona. (a) Left: Immuno...
Images
in CENP-F stabilizes kinetochore-microtubule attachments and limits dynein stripping of corona cargoes
> Journal of Cell Biology
Published: 24 March 2020
Figure 8. CENP-F-Nde1 controls corona stripping by dynein in untreated cells. (a) Immunofluorescence microscopy images of HeLa-K, CENP-F-Mut1, and CENP-F-Mut2 cells transfected with an empty vector, eGFP-CENP-F(2021–2901), or eGFP-CENP-F(2351–2901) and stained with DAPI and antibodies against More about this image found in CENP-F-Nde1 controls corona stripping by dynein in untreated cells. (a) Im...
Images
in CENP-F stabilizes kinetochore-microtubule attachments and limits dynein stripping of corona cargoes
> Journal of Cell Biology
Published: 24 March 2020
Figure 9. CENP-F-Nde1 controls corona stripping by dynein the nocodazole-monastrol assay. (a) Immunofluorescence microscopy images of the nocodazole-monastrol dynein-stripping assay in CENP-F-Mut1 and CENP-F-Mut2 cells transfected with an empty vector, eGFP-CENP-F(2021–2901), or eGFP-CENP-F More about this image found in CENP-F-Nde1 controls corona stripping by dynein the nocodazole-monastrol as...
Images
in The Microtubule-dependent Motor Centromere–associated Protein E (CENP-E) Is an Integral Component of Kinetochore Corona Fibers That Link Centromeres to Spindle Microtubules
> Journal of Cell Biology
Published: 20 October 1997
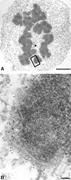
Figure 6 CENP-E is a integral component of kinetochore corona fibers extending 50 nm from the outer plate. HeLa cells were initially treated with a low dose of nocodazole for 12 h to disassemble microtubules and processed as described in Fig. 2 . Nocodazole treatment bulges the kinetochore More about this image found in CENP-E is a integral component of kinetochore corona fibers extending 50 nm...
Images
Published: 20 March 2017
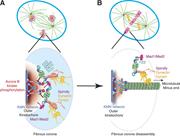
Figure 1. The Spindly–dynein–dynactin complex binds to the RZZ complex and initiates the disassembly of the fibrous corona and removal of checkpoint proteins upon kinetochore–microtubule attachment. (A) At unattached kinetochores, binding of the KMN network to microtubules is inhibited More about this image found in The Spindly–dynein–dynactin complex binds to the RZZ complex and initiates ...
Journal Articles
Alice Valagussa, Nidia Moreno-Corona, Chantal Lagresle-Peyrou, Sara Mercurio, Margot Tragin, Nicolas Goudin, Mélanie Parisot, Monica Beltrame, Despina Moshous, Sven Kracker
Journal:
Journal of Human Immunity
J Hum Immun (2025) 1 (4): e20250110.
Published: 22 October 2025
...Alice Valagussa; Nidia Moreno-Corona; Chantal Lagresle-Peyrou; Sara Mercurio; Margot Tragin; Nicolas Goudin; Mélanie Parisot; Monica Beltrame; Despina Moshous; Sven Kracker Poikiloderma with neutropenia is a genetic disorder characterized by skin abnormalities, nail dystrophy, bone anomalies...
Includes: Supplementary data
Images
in Identification of a human splenic marginal zone B cell precursor with NOTCH2-dependent differentiation properties
> Journal of Experimental Medicine
Published: 14 April 2014
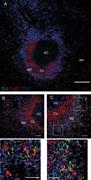
image (out of three splenic samples analyzed) of a GC surrounded by densely distributed IgD+CD27− naive cells forming the corona and the MZ at the periphery, occupied by CD27+IgDlow B cells (lightly colored in purple; splenic section of a 4-yr-old child; bar More about this image found in Non-lymphoid DLL1+ cells are located in the splenic MZ. Confoca...
Journal Articles
In Special Collection:
B Cell Biology in Health and Diseases
Romane Thouenon, Loïc Chentout, Nidia Moreno-Corona, Lucie Poggi, Emilia Puig Lombardi, Benedicte Hoareau, Yohann Schmitt, Chantal Lagresle-Peyrou, Jacinta Bustamante, Isabelle André, Marina Cavazzana, Anne Durandy, Jean-Laurent Casanova, Lionel Galicier, Jehane Fadlallah, Alain Fischer, Sven Kracker
Journal:
Journal of Experimental Medicine
J Exp Med (2023) 220 (6): e20221292.
Published: 14 March 2023
...Romane Thouenon; Loïc Chentout; Nidia Moreno-Corona; Lucie Poggi; Emilia Puig Lombardi; Benedicte Hoareau; Yohann Schmitt; Chantal Lagresle-Peyrou; Jacinta Bustamante; Isabelle André; Marina Cavazzana; Anne Durandy; Jean-Laurent Casanova; Lionel Galicier; Jehane Fadlallah; Alain Fischer; Sven...
Includes: Supplementary data
Journal Articles
Xiaoyi Qu, Feng Ning Yuan, Carlo Corona, Silvia Pasini, Maria Elena Pero, Gregg G. Gundersen, Michael L. Shelanski, Francesca Bartolini
Journal:
Journal of Cell Biology
J Cell Biol (2017) 216 (10): 3161–3178.
Published: 06 September 2017
...Xiaoyi Qu; Feng Ning Yuan; Carlo Corona; Silvia Pasini; Maria Elena Pero; Gregg G. Gundersen; Michael L. Shelanski; Francesca Bartolini Oligomeric Amyloid β1–42 (Aβ) plays a crucial synaptotoxic role in Alzheimer’s disease, and hyperphosphorylated tau facilitates Aβ toxicity. The link...
Includes: Supplementary data
Journal Articles
In Special Collection:
RNA
Désirée Schatton, David Pla-Martin, Marie-Charlotte Marx, Henriette Hansen, Arnaud Mourier, Ivan Nemazanyy, Alberto Pessia, Peter Zentis, Teresa Corona, Vangelis Kondylis, Esther Barth, Astrid C. Schauss, Vidya Velagapudi, Elena I. Rugarli
Journal:
Journal of Cell Biology
J Cell Biol (2017) 216 (3): 675–693.
Published: 10 February 2017
...Désirée Schatton; David Pla-Martin; Marie-Charlotte Marx; Henriette Hansen; Arnaud Mourier; Ivan Nemazanyy; Alberto Pessia; Peter Zentis; Teresa Corona; Vangelis Kondylis; Esther Barth; Astrid C. Schauss; Vidya Velagapudi; Elena I. Rugarli Mitochondria are essential organelles that host crucial...
Includes: Supplementary data
Images
Published: 06 October 2022
. As part of the fibrous corona, DYNEIN-DYNACTIN-SPINDLY assists in chromosome movement. Later in metaphase, the motor complex also contributes to corona disassembly by promoting RZZ removal from kinetochores. More about this image found in Conformational changes in SPINDLY control DYNEIN activation at kinetochores...
1
Advertisement